(ISSN 2300-1496)

(ISSN 2300-1496)
(ISSN 2300-1496)

(ISSN 2300-1496)

(ISSN 2300-1496)

(ISSN 2300-1496)
(ISSN 2300-1496)
The first issue, No. 1

The second issue, No. 2



The first issue, No. 1 (2024)
An attempt to apply management methods to the cost optimisation of modular construction
 Corresponding author
Corresponding author
DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.15576/GLL/2024.1.01
Nowadays, many management methods are used in the implementation of investment processes. Their common attribute is optimising the total cost of implementing an investment
project by reducing all types of costs at each stage of the process. This is particularly important if the investment process is very complex since it is implemented according to the idea of modular construction. The aim of this study is to identify those modern management methods that improve the investment process by leading to the optimisation of the costs involved. These methods refer to the management process of the investment project (Agile Scrum Method, Kanban Method, Lean Construction Method) or directly to the management of the costs generated by the project (Activity-Based Costing). Together these methods will contribute to optimising the total cost of the project. Moreover, their applicability means they can be directly implemented or modified in any investment project that utilises modular construction. The features of the mentioned methods were identified and adapted to the specificity and requirements of the investment process in modular construction using the desk research method. As a result, it has been noticed that the use of management methods such as Agile Scrum, Lean Construction and ABC are crucial in the implementation of modular construction projects due to their ability to streamline processes, increase cost and time efficiency, and enable flexibility in the event of changing requirements.
Keywords: modular construction • cost optimisation • Activity-Based Costing • Lean Construction Method • Agile Scrum Method
Monika Mika 
![]() , Katarzyna Fortuna, Monika Siejka
, Katarzyna Fortuna, Monika Siejka ![]()
Comparative analysis of the formal and legal principles of easements in Poland
 Corresponding author
Corresponding author
DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.15576/GLL/2024.1.02
This is a research-based publication. It compiles an up-to-date knowledge on the issues concerning easement law in Poland. The research framework for examining the principles of determining the easement right, as one of several limited property rights occurring in the Polish legal system, allowed the authors to develop the features of easement appurtenant, personal easement, and transmission line easement in a descriptive and graphical form. The authors pay particular attention to the differences in the formal and legal principles applicable to the establishment and enforcement of different types of easements in Poland. Therefore, this paper distinguishes and extensively discusses the two most common easement cases. The first one concerns the right-of-way easement, which according to formal and legal principles is a type of easement appurtenant. The second is an easement of habitation (which is a special type of personal easement). Furthermore, the paper analyses the formal and legal prerequisites for the creation of the easement appurtenant and personal easement. The aim of the research was to draw attention to the complexity of the easement law in Poland and to provide a thematic systematisation of related concepts. Methods based on the principles of descriptive-comparative analysis allowed to achieve the research objective. For a better understanding of the presented subject by the reader, the “introduction” section includes key definitions, formal and legal principles of establishing an easement, conditions of its termination, change in the content of the right, and transfer of rights to another entity. The study is based on the current state of knowledge, supported by extensive research of the subject literature on the presented research topic and the interpretation of the binding legal regulations.
Keywords: limited property rights • types of easements • legislation • property valuation
Przemysław Klapa 
![]() , Bartosz Mitka
, Bartosz Mitka ![]() , Dawid Duraziński, Mateusz Zagórowski, Aleksandra Podżorska
, Dawid Duraziński, Mateusz Zagórowski, Aleksandra Podżorska
Use of terrestrial laser scanning point cloud in the inventory of Mechowo Caves
 Corresponding author
Corresponding author
DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.15576/GLL/2024.1.03
An inventory is a set of technical operations for obtaining reliable information about a site in order to prepare technical and descriptive documentation, presenting the current state of objects. One of the measurement technologies allowing for the acquisition of reliable and comprehensive information about a site is terrestrial laser scanning. A point cloud from terrestrial laser scanning generates both 2D surveys and 3D models of various types of objects. The scope of research work included the application of terrestrial laser scanning (TLS) technology in the inventory of the Mechowo Caves – a cave in the village of Mechowo. The survey of the area in front of the
cave and its part accessible to visitors was carried out using a Leica P40 laser scanner. Due to the highly varied shape of the cave ( multiple low and narrow passages) and its unique character, the measurement had to be performed in a non-standard way – with the use of numerous measuring stations with different combinations of measuring instrument settings and variable scanning parameters. As a result of the work, a point cloud was generated, based on which cross-sections presenting the spatial layout of the Mechowo Caves were created, as well as a 3D model of the area covered by the survey.
Keywords: cave inventory • TLS • geospatial data • technical documentation • point cloud
Evaluation of heavy metals pollution in recent sediments of Zoubia Wadi, W-Skikda (NE of Algeria)
 Corresponding author
Corresponding author
DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.15576/GLL/2024.1.04
This study aims to evaluate the level of metallic pollution in the recent sediments of the Zoubia area (Aïn Kechera) in north-east of Algeria. The method used for this assessment involves sediments sampling and the determination of heavy metal concentrations. The study estimated the level of metallic pollution in the sediments by calculating several pollution indexes, including the contamination factor (CF), the enrichment factor (FE), the geo-accumulation index (Igeo), the individual ecological risk index (), the potential ecological risk (RI) and statistical analysis of the data. The study monitored seven trace metals: cadmium (Cd), chromium (Cr), nickel (Ni), lead (Pb), zinc (Zn) and copper (Cu). The results indicate an enrichment of Cd, Pb, Zn, and Cu in all samples. However, Ni, Co, and Cr levels are below those of the continental crust (background). The geo-accumulation index values for Co, Ni, and Cr are negative in all samples. On the other hand, positive geo-accumulation index values were observed for Cd, Pb, Zn, and some Cu samples (B1, B2, B3, and B4) with individual ecological risks of less than 40 for Cd, (94.48–119.21) for Zn, and (80.23–135.4) for Cu, respectively. This indicates low risk for Cd and high risk for Zn and Cu. The results indicate that Pb poses a significant ecological risk (537.4–842.05) and may have adverse effects on human health. The most significant pollutants, in order of increasing risk, are Pb, Cu, Zn, and Cd.
Keywords: Zoubia • Northeast Algeria • recent sediments • heavy metals • pollution indexes
Monika Mika 
![]() , Monika Siejka
, Monika Siejka ![]() , Andrzej Staszel
, Andrzej Staszel
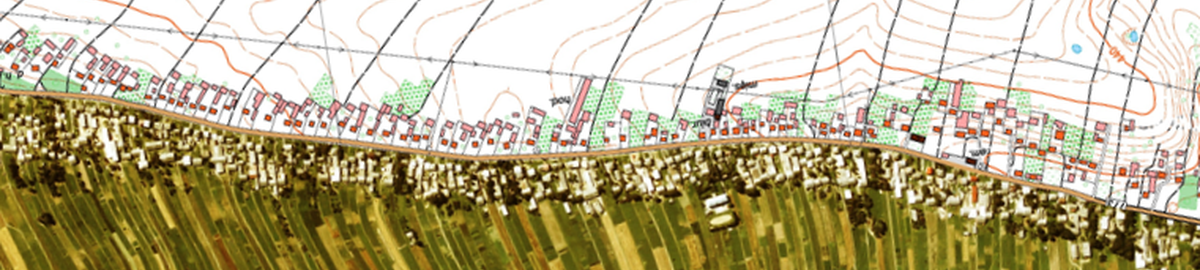
Selected aspects of spatial management in Poland in chronological perspective
 Corresponding author
Corresponding author
DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.15576/GLL/2024.1.05
This article is a part of the authors’ broader research on spatial management in Poland. Specifically, it addresses the problem of the procedures and practices of setting the planning fee on the basis of the legislation in force until 2023. The authors pay particular attention to cases of charging this fee following an increase in the value of real estate, as a consequence of changes in legislation or investment activities in a given area. In order to meet the research objective, the process of determining the planning fee was analysed on the basis of such practices over several decades. For this purpose, a detailed study of the subject literature was carried out, which included both book titles and scientific papers, as well as the interpretation of the law. The study highlighted the major role of correct and up-to-date planning documentation, both at the national and regional levels. It also identified the importance of the local spatial development plan and all the procedures for amending it. This publication consists of both analysis and research. This research resulted in a graphical presentation of many complex issues concerning spatial management in Poland, under both legal and economic aspects. It includes figures, such as a diagram of the stages of the procedure for setting the percentage rate by the municipal council, in the case of amending or adopting the local plan, the procedure for calculating the planning fee, the algorithm for increasing the value of real estate, and the procedure for refunding the planning fee. The paper also covers the issue of predicted changes in spatial policy.
Keywords: spatial management • planning fees • planning annuity
Analysis and improvement of the fragmentation quality of blasted rock using digital image processing: the case of the Kef Lahmer quarry, N-E Algeria
 Corresponding author
Corresponding author
DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.15576/GLL/2024.1.06
The mining industry plays a significant role in the extraction and processing of various ore materials (phosphate, copper, iron, gold, aggregates and others), contributing to industrial and economic development. Rock fragmentation is a fundamental operation and a complex element in mining activities influenced by multiple parameters, including geological and geometric factors, explosive load parameters, and others related to the details of the execution of the blasting plan. The effectiveness of blasting depends on factors such as the geological structure, volume, optimal size of rocks to be blasted, and compliance with safety conditions. To achieve desirable outcomes, it is crucial to make informed decisions regarding the types and quantities of explosives to be used, along with other principal parameters of drilling-blasting design. Continuous evaluation of rock fragmentation is essential for optimizing blasting plans by contributing to the improvement of the quality-price ratio under favorable environmental and safety conditions. This study aims to analyze and enhance the quality of rock fragmentation resulting from blasting activities in the Kef Lahmar-Setif limestone quarry (northeast Algeria), which is characterized by significant rock mass fracturing. This fracturing will be carefully analyzed in order to arrive at an accurate blasting plan for the structure of the studied rock massif. As the aim of the research is to optimize the blasting plan to generate maximum gas pressure and minimize shock pressure due to the existing fractures in the rock mass. in order to test this hypothesis, we conducted several blasting tests by modifying the charge rate of the explosives used (Anfomil and Marmanite III), while maintaining the same parameters in the blasting plan for each test. The goal was to achieve optimal fragmentation. The particle size of the blasted rock pile was analyzed using WipFrag software, which utilizes image analysis techniques.
Keywords: blasting • fragmented rock mass • explosives • image analysis • WipFrag
Assessment of groundwater mineralization in the arid steppe region of the Messaad plateau aquifer, Southern Algeria
 Corresponding author
Corresponding author
DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.15576/GLL/2024.1.07
Water scarcity is severely high in the North Africa and the Middle East (MENA) regions. The deterioration of water quality has an impact on the human health as well as on the development of agricultural activities, especially in arid regions, where precipitations are less frequent. The aim of this work is to identify and evaluate the chemistry of the groundwater aquifer in the region of Messaad plateau. This region is located 370 km south of Algiers in southern Algeria. A dozen of samples were collected from wells and analyzed using physic-chemical technics, and the results were processed statistically. The distribution of the conductivity values and the various chemical parameters suggest that the groundwater in the Messad wadi area is overall highly mineralized, with the EC ranging from 550 μS . cm–1 to 8790.13 μS . cm–1, with a predominance of calcium sulphate facies and calcium chloride facies. The level of mineralization noted in the southern and southeastern portions of the research area sheds light on the source of natural contamination. The SO42–, Cl– , Ca2+ , Na+ ions are the most important factors influencing the electrical conductivity of water and the groundwater chemistry. These ions are the result of the continuous dissolution of gypsum and halite in the clays and marls of the Barremian formations.
Keywords: Barremian aquifer • mineralization • groundwater origin • Messaad • Algeria
Exploring the economic significance and diverse hues of quartz: A case study at Adaila, south of El Ma Labiod, NE Algeria
 Corresponding author
Corresponding author
DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.15576/GLL/2024.1.08
The Tebessa region in Algeria is rich in mineralogical resources within its Quaternary deposits, particularly in quartz. This study adopts a multidisciplinary approach including stratigraphic, sedimentological, and granulometric analyses, focusing specifically on the deposits located in the fluvial terraces of the Oued Adaila, south of Tébessa in eastern Algeria. The analysis of granulometric parameters gave valuable insights into the uniformity of the energy levels exerted by the transport agents.
Pioneering exoscopy techniques have proved indispensable in discerning the sedimentary history of quartz, offering comprehensive insights into its weathering processes and its intricate journey through continental aquatic pathways. Additionally, this methodology has elucidated the genesis of unique colourations observed in quartz grains. Using Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM), we have examined the surfaces of quartz grains, revealing an array of patterns attributable either to the inherent crystal lattice structure of quartz or to the erosive influences of the changing environment. These environmental modifications stand out as the primary contributors to the diverse spectrum of colours manifested in the quartz grains. Furthermore, the examination of magnetic data has highlighted the pivotal role played by various
oxides present in the Quaternary deposits. These oxides proved to be important sources of ferric elements, crucial in imparting the distinct colorations observed in quartz. This comprehensive study significantly advances our understanding of the mineralogical constitution, sedimentary evolution, and the environmental dynamics shaping the Quaternary deposits in the Tebessa region.
Keywords: ferric elements • granulometric parameters • Quaternary • Oued Adaila • quartz colouring
The second issue, No. 2 (2024)
 Title page, content
Title page, content ![]() download
download
Foreword ![]() download
download
The use of modern photogrammetric techniques in the inventory of historical monuments ‒ focus on the Potocki Palace in Krzeszowice
 Corresponding author
Corresponding author
DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.15576/GLL/2024.2.01
The study presents advanced measurement methods used in the inventory of historic buildings, focused on the Potocki Palace in Krzeszowice. The paper focuses on two main measurement methods that allowed comprehensive and accurate documentation to be obtained. The first technique was terrestrial laser scanning, using specialised laser scanners to collect data. In order to reproduce the actual colours and texture of the object under study, the scanning method was supported by photogrammetry. The second method was low-ceiling photogrammetry, which provided even more accurate data about the Palace. Data processing resulted in a three-dimensional (3D) solid, consisting of a multi-million-point cloud. This was followed by a vectorisation process, which made it possible to obtain a full-dimensional representation of the studied object. The results allowed a detailed analysis of the Potocki Palace, including the identification of damage and changes occurring over the years. This documentation provides a solid basis for future conservation, modernisation and research work related to the building.
The paper also points out the potential possibilities of using modern technologies to visualize inventoried objects. The technique of Virtual Reality (VR) and showing the object in 3D, which has been popular so far, has recently found even wider possibilities giving input to the construction of so-called Augmented Reality (AR).
Keywords: photogrammetry, laser scanning, inventory of monuments, virtual reality, Potocki Palace in Krzeszowice
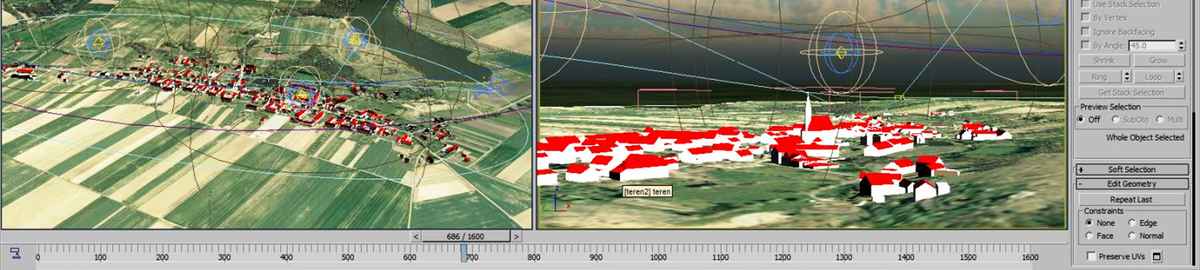
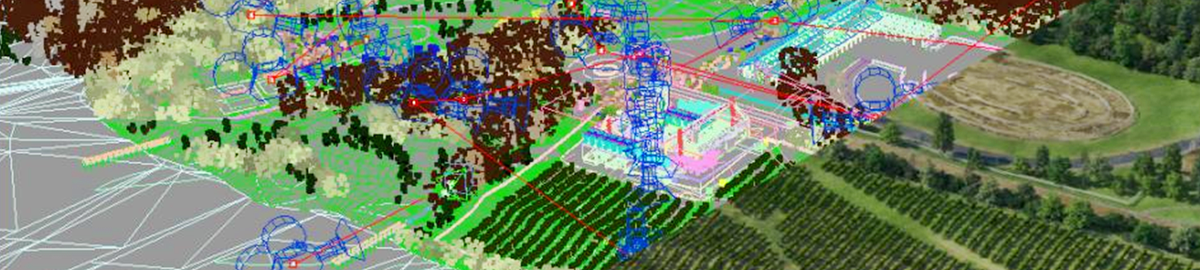
The use of artificial intelligence methods for analyzing images obtained through low-altitude photogrammetry technology to calculate the volume of mass in open-pit mines
 Corresponding author
Corresponding author
DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.15576/GLL/2024.2.02
Measurements using drones have enabled significant changes in inventorying and monitoring mining areas. Drone-based measurements can be faster and more accurate [Mazurek 2018]. Aerial photographs taken with drones allow the surveying department in mines to accurately represent the photographed terrain and make precise measurements, which can be used, among other things, to calculate the volume of mass. The aim of the article is to present the results of research on the automated process of acquiring and processing photogrammetric data for the purpose of calculating mass volumes. As part of the research, an algorithm based on classical methods and deep learning was developed.
AGH, in collaboration with the Silesian University of Technology and 3D Format company from Gliwice, has developed a system for automated volumetric measurements based on low-altitude photogrammetry using non-metric photos and artificial intelligence (AI) algorithms to provide cyclical volume measurement services on the Polish market.
The idea of the system is to acquire data automatically, then provide the data in the cloud, maximize measurement automation, and provide results in near real-time. The entire process is to be conducted using software available through the website.
The project was divided into several stages; in this publication, I want to focus on the automation of the measurement of surveying points.
Keywords: photogrammetry, UAV, artificial intelligence, open pits mines
![]()
The fourth issue, No. 3 (2024)
Coming soon...
The third issue, No. 4 (2024)
Coming soon...
Owner of the Journal
University of Agriculture in Krakow
Faculty of Environmental Engineering and Land Surveying
Balicka st., no. 253a, 30-198 Krakow, Poland
phone: +48 12 662 45 32, fax +48 12 662 45 03
e-mail: gll@urk.edu.pl
Publisher
Publishing House of the University of Agriculture in Krakow
29 Listopada av., no 46, 31-425 Kraków, Poland
phone: +48 12 662 51 51, fax +48 12 662 51 59
e-mail: wydawnictwo@urk.edu.pl
e-mail: iwona.pisiewicz@urk.edu.pl


